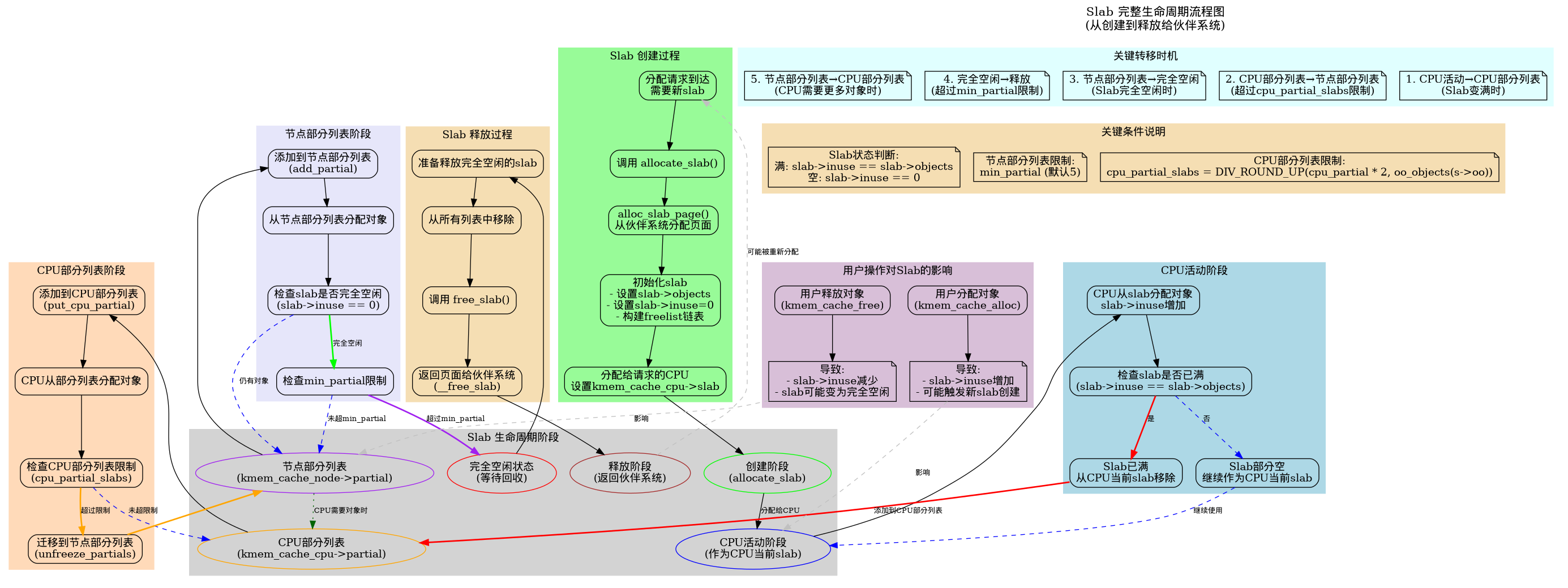
slab 位置
系统运行过程中,一个slab在某一时刻所处的位置,可能的情况如下:
- 作为满状态的slab,悬空状态,不被任何cpu或者node跟踪
- 作为满状态的slab,调试模式下,位于
node->full上 - 作为active活动slab,位于
c->slab上(slab上空闲objects由c->freelist管理 ) - 作为inactive非活动slab,位于
c->partial上 - 作为inactive非活动slab,位于
node->partial上
alloc、free、shrink等 action 都有可能触发slab的位置发生迁移。
生命周期
slab完整生命周期框架结构图
迁移状态机
共计20条位置转移路径如图所示
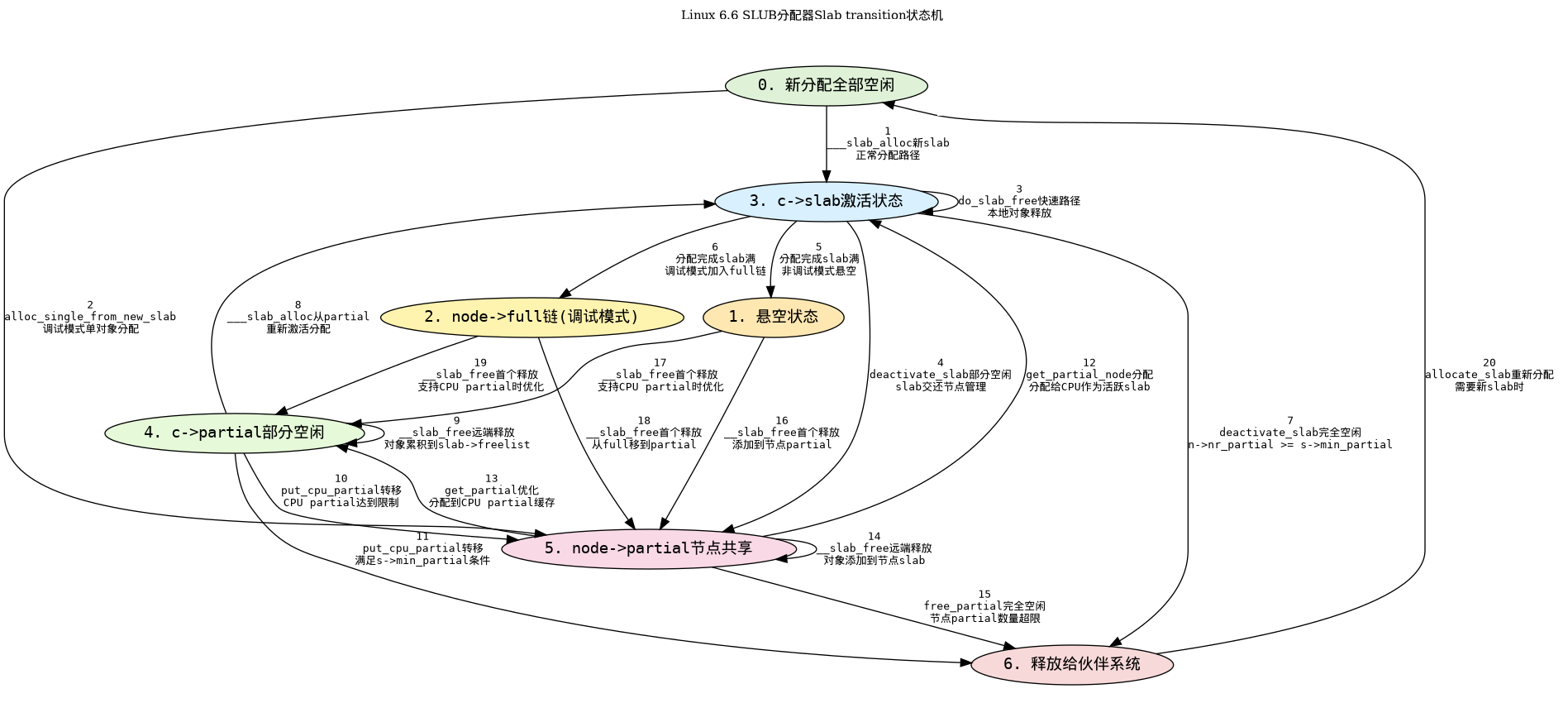
迁移说明
-
allocation-driven 转移: 1、2、5、6、8、12、13、20
分配路径(slab_alloc_node()、load_freelist()、get_partial_node()、alloc_single_from_new_slab()等)触发,
常以alloc_event为核心事件。 -
free/owner-driven 转移:3、4、7、9、10、11、14、15、16、17、18、19
do_slab_free()fast-path(3)或__slab_free()slow-path / owner 操作(deactivate_slab()、
put_cpu_partial()、remove_full()/add_partial()、discard_slab()等)触发。 -
关键布尔变量:
prior(释放前slab->freelist != NULL)区分“full” vs “partial before free”;new.inuse(释放后占用数)判定 slab 是否变空(用于丢弃);was_frozen判定 slab 是否属于某 CPU(影响远端 frees 的处理);has_cpu_partial决定 full 首次释放时走 freeze-to-cpu_partial(fast)还是 node->partial(slow);n->nr_partial >= s->min_partial决定是否会丢弃空 slab。
以下是20条 slab 动态转移路径的详细阐述:
1) S0 -> S3(新分配全部空闲 → c->slab 激活)
条件(事件+布尔): alloc_event && !c->slab && !c->partial && !n->partial
代码/说明: slab 和 cpu 关联绑定,首个 object 被分配器选中,
分配路径 slab_alloc_node() / load_freelist()
执行 c->slab = slab; c->freelist = get_freepointer(...);
2) S0 -> S5(新分配全部空闲 → node->partial,debug 单对象分配)
条件(事件+布尔): alloc_event && slub_debug
源码映射 / 说明: 在 debug / SLUB_TINY 等模式下,
分配器的单对象分配路径(alloc_single_from_new_slab() 或 debug 特殊路径)
会把刚分配的新 slab 放到 node->partial。
3) S3 -> S3(c->slab 快速路径释放:保持 active)
条件(事件+布尔): free_event && slab == c->slab && fast-path success
源码映射 / 说明: do_slab_free() fast-path:当释放发生在 owning CPU 的 active slab 并且 fast-path atomic/cmpxchg 成功时,
仅更新 c->freelist 并返回;不会进行 __slab_free() 的慢路径链表操作。
4) S3 -> S5(deactivate_event)
条件(事件+布尔): owner_action (deactivate_slab / retry_load_slab flush)或者出现并发处理
代码/说明: owner CPU 决定 flush/deactivate(例如 retry_load_slab 中 flush,
或 deactivate_slab() 被调用以把 active slab 和 CPU 解绑),
CPU 会把 slab 交回 node 层(add_partial() )。
5) S3 -> S1(c->slab 被分配耗尽 → 悬空)
条件(事件+布尔): alloc_event && slab->inuse == slab->objects
源码映射 / 说明: 连续分配把 slab 中所有对象分配完,属于 allocation 驱动。
6) S3 -> S2(c->slab 被分配耗尽 → node->full(debug))
条件(事件+布尔): alloc_event && slab->inuse == slab->objects && debug
源码映射 / 说明: 与 5 类似,但当 debug(或 SLUB_TINY/kmem_cache_debug)打开时,
full slab 会被记录到 node->full 以便调试跟踪。代码路径在调试分支。
属于 allocation 驱动。
7) S3 -> S6(c->slab → 丢弃/返还给伙伴)
条件(事件+布尔): owner_action && new.inuse == 0 && n->nr_partial >= s->min_partail
源码映射 / 说明:当 owner 在 deactivate/flush 路径或慢路径判断到 slab 在释放后变空(new.inuse == 0)
并且 node 要求丢弃(n->nr_partial >= s->min_partial),则走 slab_empty 分支并调用 discard_slab(),把页返还给伙伴系统。
这是 owner/slow-path 决定的,不是单纯的 fast-path free。
8) S4 -> S3(c->partial → c->slab,被激活)
条件(事件+布尔): alloc_event && was_frozen == 1
源码映射 / 说明: CPU 从它的 cpu_partial(frozen slab)中挑选 slab 并激活(load_freelist())。
9) S4 -> S4(c->partial 上的远端释放)
条件(事件+布尔): free_event && was_frozen == 1
源码映射 / 说明: slab 已冻结属于某 CPU(was_frozen==1),
远端 CPU 的 frees 会把对象加入该 slab 的 slab->freelist,
但 slab 仍挂在远端 CPU 的 cpu_partial ,仅内部 freelist 变更。
10) S4 -> S5(从 cpu_partial 转移到 node->partial)
条件(事件+布尔): owner_action 或 oldslab->slabs >= s->cpu_partial_slabs
源码映射 / 说明: 当 owner CPU 决定回收/flush 部分空 slab 并且满足oldslab->slabs >= s->cpu_partial_slabs
会把 frozen slab 从 cpu_partial 转移到 node->partial(put_cpu_partial() 路径)。
这是free-driven 释放事件驱动的。
11) S4 -> S6(c->partial slab 完全空且被丢弃)
条件(事件+布尔): free_event && new.inuse == 0 && n->nr_partial >= s->min_partail
源码映射 / 说明: 当 frozen slab 在某次释放后变空(new.inuse==0)并且 node 决定可以回收(n->nr_partial >= s->min_partail),
就会执行 discard_slab(),将页返还给伙伴。条件与 __slab_free() 中 slab_empty 分支一致。
12) S5 -> S3(node->partial → c->slab,被 CPU 取为 active)
条件(事件+布尔): alloc_event && prior != NULL
源码映射 / 说明: 如果 CPU 从 node->partial 获取到 slab,
并且该 slab 在获取前是 partial非空,则激活为 active slab(get_partial_node() / load_freelist() 执行路径)。
由allocation-driven 分配事件驱动。
13) S5 -> S4(node->partial → c->partial,owner 取回并 freeze)
条件(事件+布尔): alloc_event && has_cpu_partial
源码映射 / 说明: 如果系统支持 per-CPU partial (has_cpu_partial==true),
CPU 从 node partial 取得 slab 时,不是立刻激活,而把 slab 冻结并放到自己的 cpu_partial(put_cpu_partial())。
allocation-driven分配事件 和 has_cpu_partial 策略共同驱动的。
14) S5 -> S5(node->partial 上的远端释放)
条件(事件+布尔): free_event && !was_frozen
源码映射 / 说明: 当 slab 在 node->partial上未冻结(was_frozen==0)时,
任何 CPU 的 free(slow-path)都会更新该 slab 的 slab->freelist,但 slab 位置仍在 node partial 不变,
只是更新 node->freelist (__slab_free() slow-path 的常见情况)。
15) S5 -> S6(node->partial slab 变空并被丢弃)
条件(事件+布尔): free_event && new.inuse == 0 && n->nr_partial >= s->min_partail
源码映射 / 说明: __slab_free() 的 slab_empty 分支下若发现 new.inuse==0 且 n->nr_partial >= s->min_partial(超过限制),
则从 node partial 中移除并调用 discard_slab() 回收 page。
16) S1 -> S5(悬空slab首个object被释放 → node->partial)
条件(事件+布尔): free_event && !was_frozen && !prior && !has_cpu_partial
源码映射 / 说明: !prior 表示释放前 slab->freelist == NULL(slab 为 full)。
slab 未被冻结(!was_frozen)且系统不支持 cpu partial(!has_cpu_partial),
__slab_free() 在慢路径会拿 node 锁并执行 remove_full() / add_partial() ,将 slab 插入 node->partial。
slab上的首个object 被 free 就导致 sla b从 n->full 转移到 n->partial。
17) S1 -> S4(full 首个释放 + 支持 CPU partial → freeze 放 cpu_partial)
条件(事件+布尔): free_event && !was_frozen && !prior && has_cpu_partial
源码映射 / 说明: 当 full slab 收到首个object被 free(!prior)且支持 cpu partial,
释放者会把 slab 冻结(new.frozen=1)并最终通过快速路径 put_cpu_partial() ,
把 slab 放到该 CPU 的 cpu_partial,这是发生在慢路径里并由释放者 freeze slab。
18) S2 -> S5(node->full(debug)首次释放object → node->partial)
条件(事件+布尔): debug && free_event && !prior
源码映射 / 说明: 在 debug 模式 node->full 链上的 slab 上的object 第一次 free(!prior)时,
debug 路径(例如 free_to_partial_list() 或专门的 debug 处理)会将 slab 从 n->full 列表移到 n->partial。
19) S2 -> S4(node->full(debug)首个释放 + CPU partial → cpu_partial)
条件(事件+布尔): debug && free_event && !prior && has_cpu_partial
源码映射 / 说明: 类似于 18,但若 has_cpu_partial 为真,
debug 首次 free 会把 slab freeze 并把它交给某 CPU 的 cpu_partial(new.frozen=1 + put_cpu_partial())。
20) S6 -> S0(申请新的 slab)
条件(事件+布尔): alloc_event(page 被 page-allocator 重新分配并用于构建新 slab)
源码映射 / 说明: discard_slab() 释放页后,page allocator 未来可能重新分配该页,
并在 slab 初始化路径产生一个全新且全部空闲的 slab。这是 page-allocation / slab 初始化驱动的转换。
代码映射
上面20条转移路线在代码中的映射位置标记如下
static void *get_partial_node(struct kmem_cache *s, struct kmem_cache_node *n,
struct partial_context *pc)
{
struct slab *slab, *slab2;
void *object = NULL;
unsigned long flags;
unsigned int partial_slabs = 0;
/*
* Racy check. If we mistakenly see no partial slabs then we
* just allocate an empty slab. If we mistakenly try to get a
* partial slab and there is none available then get_partial()
* will return NULL.
*/
if (!n || !n->nr_partial)
return NULL;
spin_lock_irqsave(&n->list_lock, flags);
list_for_each_entry_safe(slab, slab2, &n->partial, slab_list) {
void *t;
if (!pfmemalloc_match(slab, pc->flags))
continue;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SLUB_TINY) || kmem_cache_debug(s)) {
object = alloc_single_from_partial(s, n, slab,
pc->orig_size);
if (object)
break;
continue;
}
t = acquire_slab(s, n, slab, object == NULL);
if (!t)
break;
// -------------- 12.a 获取的部分空闲slab 已经从node->partial上移除
if (!object) {
*pc->slab = slab; // -------------- 12.b 传递出去返回给__slab_alloc中的slab
stat(s, ALLOC_FROM_PARTIAL);
object = t;
} else {
put_cpu_partial(s, slab, 0); // -------------- 13 debug模式或者定义了SLUB_TINY
stat(s, CPU_PARTIAL_NODE);
partial_slabs++;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SLUB_CPU_PARTIAL
if (!kmem_cache_has_cpu_partial(s)
|| partial_slabs > s->cpu_partial_slabs / 2)
break;
#else
break;
#endif
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
return object;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SLUB_CPU_PARTIAL
static void __unfreeze_partials(struct kmem_cache *s, struct slab *partial_slab)
{
struct kmem_cache_node *n = NULL, *n2 = NULL;
struct slab *slab, *slab_to_discard = NULL;
unsigned long flags = 0;
while (partial_slab) {
struct slab new;
struct slab old;
slab = partial_slab;
partial_slab = slab->next;
n2 = get_node(s, slab_nid(slab));
if (n != n2) {
if (n)
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
n = n2;
spin_lock_irqsave(&n->list_lock, flags);
}
do {
old.freelist = slab->freelist;
old.counters = slab->counters;
VM_BUG_ON(!old.frozen);
new.counters = old.counters;
new.freelist = old.freelist;
new.frozen = 0;
} while (!__slab_update_freelist(s, slab,
old.freelist, old.counters,
new.freelist, new.counters,
"unfreezing slab"));
if (unlikely(!new.inuse && n->nr_partial >= s->min_partial)) {
slab->next = slab_to_discard; // -------------- 11.a n->partial 链上空闲slab个数超过限制
slab_to_discard = slab;
} else {
add_partial(n, slab, DEACTIVATE_TO_TAIL); // -------------- 10.d slab 进入node->partial链表
stat(s, FREE_ADD_PARTIAL);
}
}
if (n)
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
while (slab_to_discard) {
slab = slab_to_discard;
slab_to_discard = slab_to_discard->next;
stat(s, DEACTIVATE_EMPTY);
discard_slab(s, slab); // -------------- 11.b 释放slab给伙伴系统
stat(s, FREE_SLAB);
}
}
/*
* Unfreeze all the cpu partial slabs.
*/
static void unfreeze_partials(struct kmem_cache *s)
{
struct slab *partial_slab;
unsigned long flags;
local_lock_irqsave(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
partial_slab = this_cpu_read(s->cpu_slab->partial);
this_cpu_write(s->cpu_slab->partial, NULL);
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
if (partial_slab)
__unfreeze_partials(s, partial_slab);
}
static __always_inline void do_slab_free(struct kmem_cache *s,
struct slab *slab, void *head, void *tail,
int cnt, unsigned long addr)
{
void *tail_obj = tail ? : head;
struct kmem_cache_cpu *c;
unsigned long tid;
void **freelist;
redo:
/*
* Determine the currently cpus per cpu slab.
* The cpu may change afterward. However that does not matter since
* data is retrieved via this pointer. If we are on the same cpu
* during the cmpxchg then the free will succeed.
*/
c = raw_cpu_ptr(s->cpu_slab);
tid = READ_ONCE(c->tid);
/* Same with comment on barrier() in slab_alloc_node() */
barrier();
if (unlikely(slab != c->slab)) { // 远端异地释放,走慢速路径
__slab_free(s, slab, head, tail_obj, cnt, addr);
return;
}
// -------------- 3 快速路径,本地对象释放
if (USE_LOCKLESS_FAST_PATH()) {
freelist = READ_ONCE(c->freelist);
set_freepointer(s, tail_obj, freelist);
if (unlikely(!__update_cpu_freelist_fast(s, freelist, head, tid))) {
note_cmpxchg_failure("slab_free", s, tid);
goto redo;
}
} else {
/* Update the free list under the local lock */
local_lock(&s->cpu_slab->lock);
c = this_cpu_ptr(s->cpu_slab);
if (unlikely(slab != c->slab)) {
local_unlock(&s->cpu_slab->lock);
goto redo;
}
tid = c->tid;
freelist = c->freelist;
set_freepointer(s, tail_obj, freelist); // 把空闲object 插入 freelist链表
c->freelist = head;
c->tid = next_tid(tid);
local_unlock(&s->cpu_slab->lock);
}
stat(s, FREE_FASTPATH);
}
static void put_cpu_partial(struct kmem_cache *s, struct slab *slab, int drain)
{
struct slab *oldslab;
struct slab *slab_to_unfreeze = NULL;
unsigned long flags;
int slabs = 0;
local_lock_irqsave(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
oldslab = this_cpu_read(s->cpu_slab->partial);
if (oldslab) {
if (drain && oldslab->slabs >= s->cpu_partial_slabs) { // -------------- 10.a cpu->partial链上slab个数超过cpu_partial_slabs 个数限制
/*
* Partial array is full. Move the existing set to the
* per node partial list. Postpone the actual unfreezing
* outside of the critical section.
*/
slab_to_unfreeze = oldslab; // -------------- 10.b 待会解冻
oldslab = NULL;
} else {
slabs = oldslab->slabs; // -------------- 17 / 19
}
}
slabs++;
slab->slabs = slabs;
slab->next = oldslab; // -------------- 17 / 19
this_cpu_write(s->cpu_slab->partial, slab);
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
if (slab_to_unfreeze) {
__unfreeze_partials(s, slab_to_unfreeze); // -------------- 10.c 进入解冻流程
stat(s, CPU_PARTIAL_DRAIN);
}
}
static void __slab_free(struct kmem_cache *s, struct slab *slab,
void *head, void *tail, int cnt,
unsigned long addr)
{
void *prior;
int was_frozen;
struct slab new;
unsigned long counters;
struct kmem_cache_node *n = NULL;
unsigned long flags;
stat(s, FREE_SLOWPATH);
if (kfence_free(head))
return;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SLUB_TINY) || kmem_cache_debug(s)) {
free_to_partial_list(s, slab, head, tail, cnt, addr); // -------------- 18
return;
}
do {
if (unlikely(n)) {
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
n = NULL;
}
prior = slab->freelist;
counters = slab->counters;
set_freepointer(s, tail, prior);
new.counters = counters;
was_frozen = new.frozen;
new.inuse -= cnt;
if ((!new.inuse || !prior) && !was_frozen) {
if (kmem_cache_has_cpu_partial(s) && !prior) {
/*
* Slab was on no list before and will be
* partially empty
* We can defer the list move and instead
* freeze it.
*/
new.frozen = 1;
} else { /* Needs to be taken off a list */
n = get_node(s, slab_nid(slab));
/*
* Speculatively acquire the list_lock.
* If the cmpxchg does not succeed then we may
* drop the list_lock without any processing.
*
* Otherwise the list_lock will synchronize with
* other processors updating the list of slabs.
*/
spin_lock_irqsave(&n->list_lock, flags);
}
}
} while (!slab_update_freelist(s, slab,
prior, counters,
head, new.counters,
"__slab_free"));
if (likely(!n)) {
if (likely(was_frozen)) {
/*
* The list lock was not taken therefore no list
* activity can be necessary.
*/
stat(s, FREE_FROZEN); // -------------- 9 远端cpu异地释放,object 插入c->partial->freelist
} else if (new.frozen) {
/*
* If we just froze the slab then put it onto the
* per cpu partial list.
*/
put_cpu_partial(s, slab, 1); // -------------- 17 / 19
stat(s, CPU_PARTIAL_FREE);
}
// -------------- 14 slab 原本非冻结、并且也不是新冻结的,那么原来就位于节点 partial 链表,现在继续待在上面即可
return;
}
if (unlikely(!new.inuse && n->nr_partial >= s->min_partial))
goto slab_empty; // node 上partial slab 个数超过kmem cache允许的最小值
/*
* Objects left in the slab. If it was not on the partial list before
* then add it.
*/
if (!kmem_cache_has_cpu_partial(s) && unlikely(!prior)) {
remove_full(s, n, slab); -------------- 16 不支持CONFIG_SLUB_CPU_PARTAIL,放入node->partial
add_partial(n, slab, DEACTIVATE_TO_TAIL);
stat(s, FREE_ADD_PARTIAL);
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
return;
slab_empty:
if (prior) {
/*
* Slab on the partial list.
*/
remove_partial(n, slab);
stat(s, FREE_REMOVE_PARTIAL);
} else {
/* Slab must be on the full list */
remove_full(s, n, slab);
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
stat(s, FREE_SLAB);
discard_slab(s, slab); -------------- 15
}
static void *alloc_single_from_partial(struct kmem_cache *s,
struct kmem_cache_node *n, struct slab *slab, int orig_size)
{
void *object;
lockdep_assert_held(&n->list_lock);
object = slab->freelist;
slab->freelist = get_freepointer(s, object);
slab->inuse++;
if (!alloc_debug_processing(s, slab, object, orig_size)) {
remove_partial(n, slab);
return NULL;
}
if (slab->inuse == slab->objects) { // slab objects全部分配完毕,没有空闲的了
remove_partial(n, slab);
add_full(s, n, slab); // -------------- 6.b 调试模式下加入node->full链表
}
return object;
}
static void *alloc_single_from_new_slab(struct kmem_cache *s,
struct slab *slab, int orig_size)
{
int nid = slab_nid(slab);
struct kmem_cache_node *n = get_node(s, nid);
unsigned long flags;
void *object;
object = slab->freelist;
slab->freelist = get_freepointer(s, object);
slab->inuse = 1;
if (!alloc_debug_processing(s, slab, object, orig_size))
/*
* It's not really expected that this would fail on a
* freshly allocated slab, but a concurrent memory
* corruption in theory could cause that.
*/
return NULL;
spin_lock_irqsave(&n->list_lock, flags);
if (slab->inuse == slab->objects) // slab objects全部分配完毕,没有空闲的了
add_full(s, n, slab); // -------------- 6.a 调试模式下加入node->full链表
else
add_partial(n, slab, DEACTIVATE_TO_HEAD); // -------------- 2.b 加入node->partial
inc_slabs_node(s, nid, slab->objects);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
return object;
}
解除一个slab与CPU的关联(即解除激活),并将该slab放到合适的管理链表中(部分空闲链表或完全空闲链表),或者释放给伙伴系统
static void deactivate_slab(struct kmem_cache *s, struct slab *slab,
void *freelist)
{
enum slab_modes { M_NONE, M_PARTIAL, M_FREE, M_FULL_NOLIST };
struct kmem_cache_node *n = get_node(s, slab_nid(slab));
int free_delta = 0;
enum slab_modes mode = M_NONE;
void *nextfree, *freelist_iter, *freelist_tail;
int tail = DEACTIVATE_TO_HEAD;
unsigned long flags = 0;
struct slab new;
struct slab old;
if (slab->freelist) {
stat(s, DEACTIVATE_REMOTE_FREES);
tail = DEACTIVATE_TO_TAIL;
}
/*
* Stage one: Count the objects on cpu's freelist as free_delta and
* remember the last object in freelist_tail for later splicing.
*/
freelist_tail = NULL;
freelist_iter = freelist;
while (freelist_iter) {
nextfree = get_freepointer(s, freelist_iter);
/*
* If 'nextfree' is invalid, it is possible that the object at
* 'freelist_iter' is already corrupted. So isolate all objects
* starting at 'freelist_iter' by skipping them.
*/
if (freelist_corrupted(s, slab, &freelist_iter, nextfree))
break;
freelist_tail = freelist_iter;
free_delta++;
freelist_iter = nextfree;
}
/*
* Stage two: Unfreeze the slab while splicing the per-cpu
* freelist to the head of slab's freelist.
*
* Ensure that the slab is unfrozen while the list presence
* reflects the actual number of objects during unfreeze.
*
* We first perform cmpxchg holding lock and insert to list
* when it succeed. If there is mismatch then the slab is not
* unfrozen and number of objects in the slab may have changed.
* Then release lock and retry cmpxchg again.
*/
redo:
old.freelist = READ_ONCE(slab->freelist);
old.counters = READ_ONCE(slab->counters);
VM_BUG_ON(!old.frozen);
/* Determine target state of the slab */
new.counters = old.counters;
if (freelist_tail) {
new.inuse -= free_delta;
set_freepointer(s, freelist_tail, old.freelist);
new.freelist = freelist;
} else
new.freelist = old.freelist;
new.frozen = 0;
//
if (!new.inuse && n->nr_partial >= s->min_partial) {
mode = M_FREE; // -------------- 7.a 完全空闲slab,并且node上partial slab个数超出min_partail 限制,准备释放
} else if (new.freelist) {
mode = M_PARTIAL;
/*
* Taking the spinlock removes the possibility that
* acquire_slab() will see a slab that is frozen
*/
spin_lock_irqsave(&n->list_lock, flags);
} else {
mode = M_FULL_NOLIST;
}
if (!slab_update_freelist(s, slab,
old.freelist, old.counters,
new.freelist, new.counters,
"unfreezing slab")) {
if (mode == M_PARTIAL)
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
goto redo;
}
if (mode == M_PARTIAL) {
add_partial(n, slab, tail);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&n->list_lock, flags);
stat(s, tail);
} else if (mode == M_FREE) {
stat(s, DEACTIVATE_EMPTY);
discard_slab(s, slab); // -------------- 7.b 释放给伙伴系统
stat(s, FREE_SLAB);
} else if (mode == M_FULL_NOLIST) {
stat(s, DEACTIVATE_FULL);
}
}
static void *___slab_alloc(struct kmem_cache *s, gfp_t gfpflags, int node,
unsigned long addr, struct kmem_cache_cpu *c, unsigned int orig_size)
{
void *freelist;
struct slab *slab;
unsigned long flags;
struct partial_context pc;
stat(s, ALLOC_SLOWPATH);
reread_slab:
slab = READ_ONCE(c->slab);
if (!slab) { // -------------- 1.a 先看kmem_cache_cpu->slab是否存在 不存在就跳转到new_slab分配新的slab
/*
* if the node is not online or has no normal memory, just
* ignore the node constraint
*/
if (unlikely(node != NUMA_NO_NODE &&
!node_isset(node, slab_nodes)))
node = NUMA_NO_NODE;
goto new_slab;
}
redo: // 走到这里,说明c->slab存在
if (unlikely(!node_match(slab, node))) {
/*
* same as above but node_match() being false already
* implies node != NUMA_NO_NODE
*/
if (!node_isset(node, slab_nodes)) {
node = NUMA_NO_NODE;
} else {
stat(s, ALLOC_NODE_MISMATCH);
goto deactivate_slab; // -------------- 4.a slab所属node和指定申请内存的node号不匹配
}
}
/*
* By rights, we should be searching for a slab page that was
* PFMEMALLOC but right now, we are losing the pfmemalloc
* information when the page leaves the per-cpu allocator
*/
if (unlikely(!pfmemalloc_match(slab, gfpflags)))
goto deactivate_slab; // -------------- 4.b 极少触发路径 紧急预留相关
/* must check again c->slab in case we got preempted and it changed */
local_lock_irqsave(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
if (unlikely(slab != c->slab)) {
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
goto reread_slab;
}
freelist = c->freelist;
if (freelist) // 如果c->freelist不存在,说明已经分配完了;如果存在跳转到load_freelist
goto load_freelist;
freelist = get_freelist(s, slab); // 查看slab->freelist是否有空闲object
if (!freelist) {
c->slab = NULL; // 走到这里说明c->slab存在,但是c->slab->freelist上没有空闲object
c->tid = next_tid(c->tid);
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
stat(s, DEACTIVATE_BYPASS);
goto new_slab; // slab->freelist上也没有空闲object,跳转到new_slab去申请
}
stat(s, ALLOC_REFILL);
load_freelist:
lockdep_assert_held(this_cpu_ptr(&s->cpu_slab->lock));
/*
* freelist is pointing to the list of objects to be used.
* slab is pointing to the slab from which the objects are obtained.
* That slab must be frozen for per cpu allocations to work.
*/
VM_BUG_ON(!c->slab->frozen);
// slab上的空闲对象都转到c->freelist上管理
c->freelist = get_freepointer(s, freelist); // -------------- 1.g
c->tid = next_tid(c->tid); // -------------- 5 slab所有objects分配完,悬空
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
return freelist;
deactivate_slab:
local_lock_irqsave(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
if (slab != c->slab) {
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
goto reread_slab;
}
freelist = c->freelist;
c->slab = NULL;
c->freelist = NULL;
c->tid = next_tid(c->tid);
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
deactivate_slab(s, slab, freelist);
new_slab:
if (slub_percpu_partial(c)) { // -------------- 1.b 再看kmem_cache_cpu->partial 上是否存在部分空闲slab
local_lock_irqsave(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
if (unlikely(c->slab)) {
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
goto reread_slab;
}
if (unlikely(!slub_percpu_partial(c))) {
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
/* we were preempted and partial list got empty */
goto new_objects;
}
slab = c->slab = slub_percpu_partial(c); // -------------- 8 重新激活slab
slub_set_percpu_partial(c, slab);
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
stat(s, CPU_PARTIAL_ALLOC);
goto redo;
}
// kmem_cache_cpu->partial 不存在部分空闲slab
new_objects:
pc.flags = gfpflags;
pc.slab = &slab;
pc.orig_size = orig_size;
freelist = get_partial(s, node, &pc); // -------------- 1.c 再看node->partial 上是否存在
if (freelist)
goto check_new_slab; //-------------- 12.c 此时slab已经指向 node->partial上移除的slab
slub_put_cpu_ptr(s->cpu_slab);
slab = new_slab(s, gfpflags, node); // -------------- 1.d c->freelist / c->partial / node->partial 均不存在空闲object,分配新的slab
// -------------- 20 new_slab从伙伴系统分配
c = slub_get_cpu_ptr(s->cpu_slab);
if (unlikely(!slab)) {
slab_out_of_memory(s, gfpflags, node);
return NULL;
}
stat(s, ALLOC_SLAB);
if (kmem_cache_debug(s)) {
freelist = alloc_single_from_new_slab(s, slab, orig_size); // -------------- 2.a 加入node->partial
if (unlikely(!freelist))
goto new_objects;
if (s->flags & SLAB_STORE_USER)
set_track(s, freelist, TRACK_ALLOC, addr);
return freelist;
}
/*
* No other reference to the slab yet so we can
* muck around with it freely without cmpxchg
*/
freelist = slab->freelist; // -------------- 1.e 把新分配的slab上的objects都暂时挂到局部变量freelist
slab->freelist = NULL;
slab->inuse = slab->objects;
slab->frozen = 1;
inc_slabs_node(s, slab_nid(slab), slab->objects);
check_new_slab:
if (kmem_cache_debug(s)) {
/*
* For debug caches here we had to go through
* alloc_single_from_partial() so just store the tracking info
* and return the object
*/
if (s->flags & SLAB_STORE_USER)
set_track(s, freelist, TRACK_ALLOC, addr);
return freelist;
}
if (unlikely(!pfmemalloc_match(slab, gfpflags))) {
/*
* For !pfmemalloc_match() case we don't load freelist so that
* we don't make further mismatched allocations easier.
*/
deactivate_slab(s, slab, get_freepointer(s, freelist)); // -------------- 4.c 极少触发路径 紧急预留相关
return freelist;
}
retry_load_slab:
local_lock_irqsave(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
if (unlikely(c->slab)) {
void *flush_freelist = c->freelist;
struct slab *flush_slab = c->slab;
c->slab = NULL;
c->freelist = NULL;
c->tid = next_tid(c->tid);
local_unlock_irqrestore(&s->cpu_slab->lock, flags);
deactivate_slab(s, flush_slab, flush_freelist); // -------------- 4.d 其它并发路径绑定了c->slab
stat(s, CPUSLAB_FLUSH);
goto retry_load_slab;
}
c->slab = slab; // -------------- 1.f 新分配的slab作为active slab 由 c->slab 跟踪记录
// -------------- 12.d slab 从node->partial 迁移到 c->slab
goto load_freelist;
}