Preempt-RT 是一个用于嵌入式系统的补丁,旨在提高 Linux 内核的实时性能。
实时系统需要能够在实时约束下及时响应事件,同时保证系统稳定和可靠性。
Preempt-RT 补丁在 Linux 内核中引入了实时抢占,允许内核在更短的时间内响应实时事件,提高了系统的实时性能。
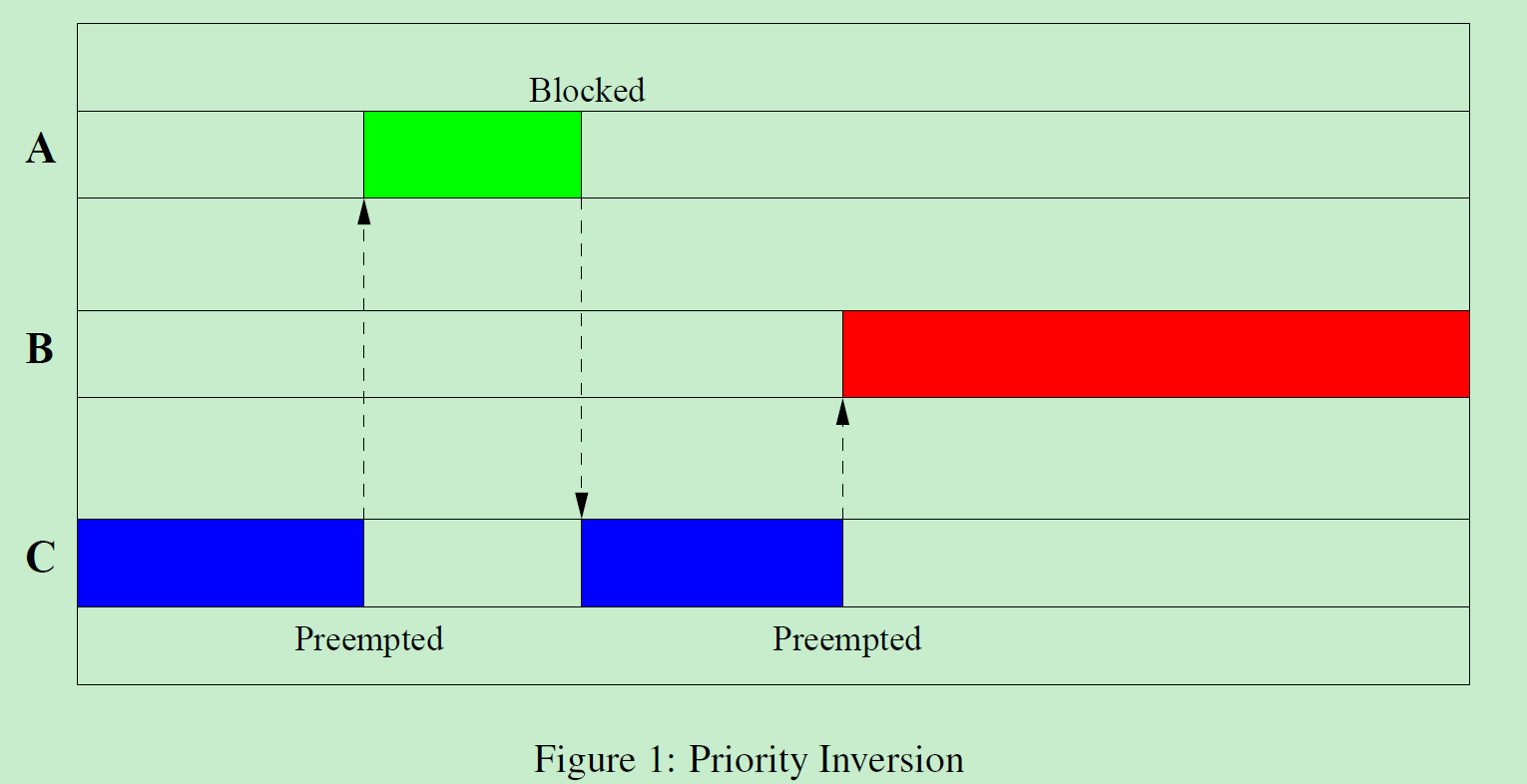
优先级反转
优先级反转是一个经典的实时系统问题,可能会影响实时系统的性能。
它发生在低优先级任务持有系统资源时,高优先级任务需要等待它完成才能获得该资源。
如果低优先级任务持有资源的时间过长,高优先级任务的响应时间将会被延迟,甚至会导致系统崩溃。
上一张图,一目了然。
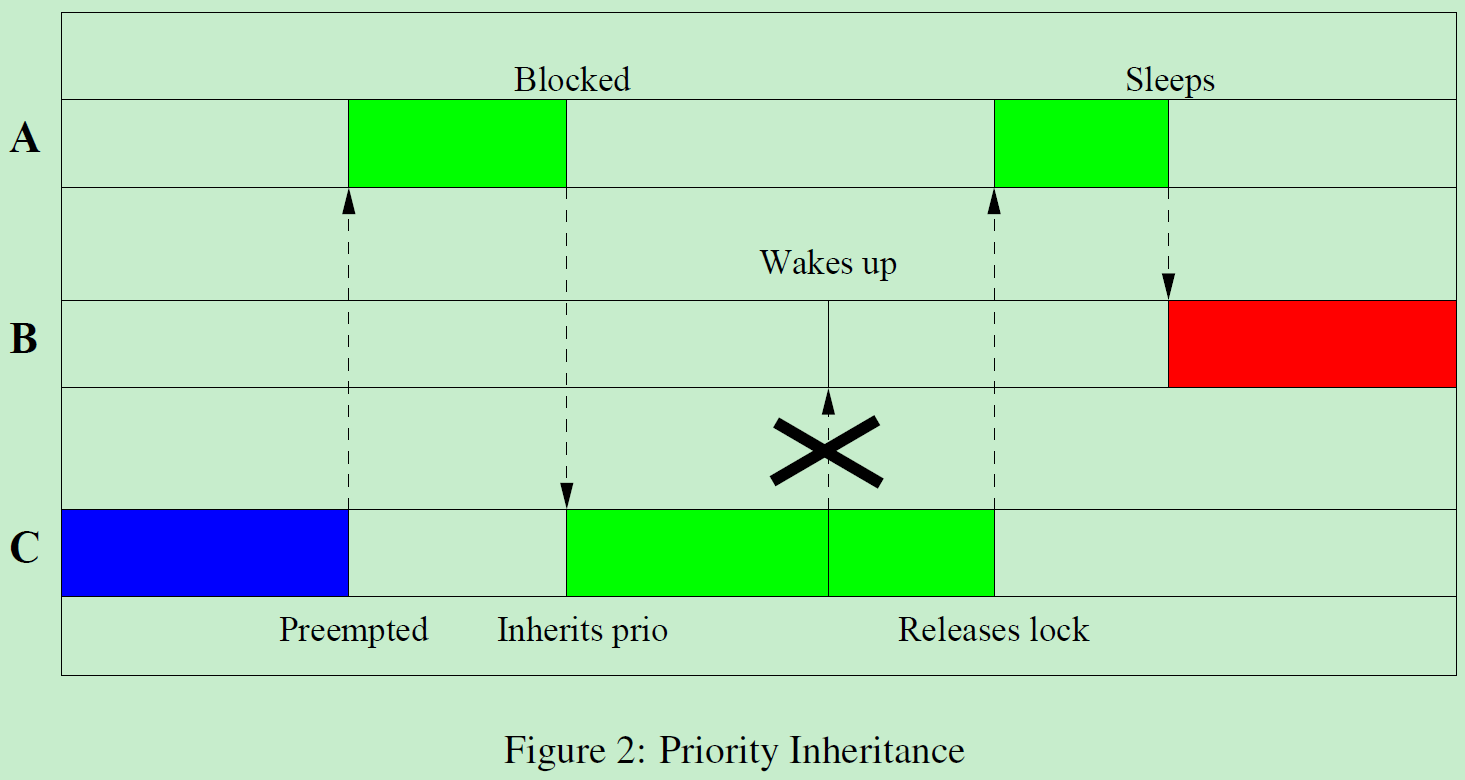
优先级继承
Preempt-RT 补丁解决了优先级反转问题,通过引入优先级继承机制,确保高优先级任务在等待系统资源时能够获取其所需的资源。
这样就能保证高优先级任务能够按时完成,并且系统稳定可靠。
相关结构体
rt_mutex
/**
* The rt_mutex structure
*
* @wait_lock: spinlock to protect the structure
* @waiters: rbtree root to enqueue waiters in priority order;
* caches top-waiter (leftmost node).
* @owner: the mutex owner
*/
struct rt_mutex {
raw_spinlock_t wait_lock; // 保护rb tree
struct rb_root_cached waiters; // 跟踪所有阻塞在该mutex上的进程,以优先级排序
struct task_struct *owner; // 如果没有被持有,该字段为NULL,可以快速判断锁是否被占
int save_state;
...
};
所有架构分配 task_struct 时保证该结构体地址至少两个字节对齐
假如owner字段的值为0xffff000011f35500 那么最低bit位可以用来作为flag标记位
bit 0可用于Has Waiters标记,任何时候有waiter时都会被置位,这样就可以强制其它进程进入 slowpath 并且在waiter_lock上等待。
RT-mutex利用这种方式区分快速路径和慢速路径,在锁无竞争或者没有waiters时,走快速路径,没有内部开销。
task_struct
struct task_struct {
...
raw_spinlock_t pi_lock; // 保护pi_waiters tree;中断上下文也会获取该锁,所以其它上下文获取pi_lock时,需要禁中断
struct rb_root_cached pi_waiters; /* PI waiters blocked on a rt_mutex held by this task: */
struct task_struct *pi_top_task; /* Updated under owner's pi_lock and rq lock */
struct rt_mutex_waiter *pi_blocked_on; /* Deadlock detection and priority inheritance handling: */
...
}
E->L4->D->L3->C-+
+->L2-+
| |
G-+ +->B->L1->A
|
F->L5-+
进程可能拿着多个锁,每个锁上可能都有多个进程阻塞在上面,那么每个锁上优先级最高的top waiters 就是PI top waiters
B进程拿着L2和L5两把锁,那么L2下游的所有等待者waiters中优先级最高的就是一个PI top waiter,
同理L5也有一个PI top waiter,这两个PI top waiters都在B进程 task->pi_waiters上挂着
rt_mutex_waiter
struct rt_mutex_waiter {
struct rb_node tree_entry; // 链接到该mutex的waiters rbtree上
struct rb_node pi_tree_entry; // 链接到持有mutex进程的pi_waiters rbtree上
struct task_struct *task; // 指向被阻塞的进程
struct rt_mutex *lock;
...
};
waiter 结构体在被阻塞进程的内核栈上分配,是个本地局部变量。
因为 waiter 的作用范围就是阻塞在 mutex 上直至所属进程被唤醒之后销毁,所以在进程栈上分配即可。
代码走读
基于linux-5.4.74-rt42
spin_lock流程
#define spin_lock(lock) rt_spin_lock(lock)
void __lockfunc rt_spin_lock(spinlock_t *lock)
{
sleeping_lock_inc();
rcu_read_lock();
migrate_disable();
spin_acquire(&lock->dep_map, 0, 0, _RET_IP_);
rt_spin_lock_fastlock(&lock->lock, rt_spin_lock_slowlock);
}
主要关注拿锁时慢速流程函数调用链
rt_spin_lock_slowlock_locked(lock, &waiter, flags);
if (__try_to_take_rt_mutex(lock, self, NULL, STEAL_LATERAL))
return;
task_blocks_on_rt_mutex(lock, waiter, self, RT_MUTEX_MIN_CHAINWALK);
next_lock = task_blocked_on_lock(owner);
//参数之间的逻辑关系: owner拿着lock,并且阻塞在next_lock; task/waiter 阻塞在lock上
rt_mutex_adjust_prio_chain(owner, chwalk, lock, next_lock, waiter, task);
rt_spin_lock_fastlock
static inline void rt_spin_lock_fastlock(struct rt_mutex *lock,
void (*slowfn)(struct rt_mutex *lock))
{
might_sleep_no_state_check();
if (likely(rt_mutex_cmpxchg_acquire(lock, NULL, current)))
return; // 把current写入lock->owner,拿锁成功,立即返回
else
slowfn(lock); // 表示锁已经被占有,需要走慢速流程 rt_spin_lock_slowlock
}
rt_spin_lock_slowlock
static void noinline __sched rt_spin_lock_slowlock(struct rt_mutex *lock)
{
struct rt_mutex_waiter waiter; // 进程栈上分配waiter空间
unsigned long flags;
rt_mutex_init_waiter(&waiter, true); // 初始化waiter结构体字段
// 先拿lock->wait_lock, 并且禁中断,安全添加当前task waiter到task waiters tree
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&lock->wait_lock, flags);
rt_spin_lock_slowlock_locked(lock, &waiter, flags);
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&lock->wait_lock, flags);
debug_rt_mutex_free_waiter(&waiter);
}
rt_spin_lock_slowlock_locked
void __sched rt_spin_lock_slowlock_locked(struct rt_mutex *lock,
struct rt_mutex_waiter *waiter,
unsigned long flags)
{
struct task_struct *lock_owner, *self = current;
struct rt_mutex_waiter *top_waiter;
int ret;
if (__try_to_take_rt_mutex(lock, self, NULL, STEAL_LATERAL))
return; // 尝试拿一次锁,成功拿到锁功就返回
BUG_ON(rt_mutex_owner(lock) == self); // 拿着锁的自己又拿同一把锁,发生死锁
......
ret = task_blocks_on_rt_mutex(lock, waiter, self, RT_MUTEX_MIN_CHAINWALK);
BUG_ON(ret);
......
}
rt_mutex_adjust_prio
检查进程优先级,该进程有可能拿着多个锁,还会检查在这些锁上等待的top waiters的优先级,然后把当前进程的优先级设置为更高的那个
该接口可能提升、也可能降低进程的优先级。比如一个更高优先级的进程阻塞了,那么持有锁的进程的优先级需要相应提升;
如果出于某种原因(超时或者信号量),高优先级的进程不再阻塞在锁上了,那么持有锁的进程的优先级就得降下来。
static void rt_mutex_adjust_prio(struct task_struct *p)
{
struct task_struct *pi_task = NULL;
lockdep_assert_held(&p->pi_lock);
if (task_has_pi_waiters(p))
pi_task = task_top_pi_waiter(p)->task; // 获取 owner的top pi waiter
rt_mutex_setprio(p, pi_task); // 根据pi_task的优先级设置owner的优先级
}
task_blocks_on_rt_mutex
- 关联current task 及其进程内核栈上对应的局部变量waiter,waiter入队到lock的红黑树上
- 如果current是lock上优先级最高的waiter,还要把current waiter入队到
owner->pi_waiters,同时调整lock owner进程的优先级 - 如果 owner 进程也阻塞在
next_lock上,还要调用rt_mutex_adjust_prio_chain继续 walk chain
static int task_blocks_on_rt_mutex(struct rt_mutex *lock,
struct rt_mutex_waiter *waiter,
struct task_struct *task,
enum rtmutex_chainwalk chwalk)
{
struct task_struct *owner = rt_mutex_owner(lock);
struct rt_mutex_waiter *top_waiter = waiter;
struct rt_mutex *next_lock;
int chain_walk = 0, res;
lockdep_assert_held(&lock->wait_lock);
/*
* Early deadlock detection. We really don't want the task to
* enqueue on itself just to untangle the mess later. It's not
* only an optimization. We drop the locks, so another waiter
* can come in before the chain walk detects the deadlock. So
* the other will detect the deadlock and return -EDEADLOCK,
* which is wrong, as the other waiter is not in a deadlock
* situation.
*/
if (owner == task) // lock的owner已经是task自己了,现在又要拿同一把lock,发生死锁
return -EDEADLK;
raw_spin_lock(&task->pi_lock);
waiter->task = task; // waiter 和 task关联
waiter->lock = lock;
waiter->prio = task->prio;
waiter->deadline = task->dl.deadline;
/* Get the top priority waiter on the lock */
if (rt_mutex_has_waiters(lock))
top_waiter = rt_mutex_top_waiter(lock); // 临时存储原来的top waiter
rt_mutex_enqueue(lock, waiter); // 把自己的waiter入队到lock的红黑树上
task->pi_blocked_on = waiter; // waiter 和 task关联
raw_spin_unlock(&task->pi_lock);
if (!owner)
return 0;
raw_spin_lock(&owner->pi_lock);
if (waiter == rt_mutex_top_waiter(lock)) { // 说明当前task waiter的优先级是最高的
rt_mutex_dequeue_pi(owner, top_waiter); // 那么把属于owner的原来的top waiter出列ownertask->pi_waiters
rt_mutex_enqueue_pi(owner, waiter); // 当前task作为owner的top waiter入列 ownertask->pi_waiters
rt_mutex_adjust_prio(owner); // 调整owner的优先级,设置为ownertask->pi_waiters所有进程里优先级最高的进程的优先级
if (rt_mutex_real_waiter(owner->pi_blocked_on)) // 如果owner阻塞在某个lock上,那么需要walk chain,因为owner的top waiter换进程了,那么owner上游也需要更新
chain_walk = 1;
} else if (rt_mutex_cond_detect_deadlock(waiter, chwalk)) { // 如果要求检测死锁,那就需要walk chain
chain_walk = 1;
}
/* Store the lock on which owner is blocked or NULL */
next_lock = task_blocked_on_lock(owner); // lock 的 owner 阻塞在next_lock上
raw_spin_unlock(&owner->pi_lock);
/*
* Even if full deadlock detection is on, if the owner is not
* blocked itself, we can avoid finding this out in the chain
* walk.
*/
if (!chain_walk || !next_lock) // 不需要walk chain 或者next_lock为NULL,即owner没有依赖的锁,无需遍历lock红黑树,返回即可
return 0;
/*
* The owner can't disappear while holding a lock,
* so the owner struct is protected by wait_lock.
* Gets dropped in rt_mutex_adjust_prio_chain()!
*/
get_task_struct(owner); // task->usage引用计数加一
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&lock->wait_lock);
res = rt_mutex_adjust_prio_chain(owner, chwalk, lock, next_lock, waiter, task); // 调整优先级链
raw_spin_lock_irq(&lock->wait_lock);
return res;
}
rt_mutex_adjust_prio_chain
- 根据需要会调整owner waiter在等待的锁next_lock->waiters 红黑树上的位置
- 如果owner优先级最高还要继续walk chain,调整上游lock owner优先级
在调用rt_mutex_adjust_prio_chain之前,增加入参task的task_struct结构体引用计数,释放lock->wait_lock
在walk chain之前,已经释放所有的lock,意即walk chain过程中进程和锁的状态是会发生变化的
函数太长,而且变量名也容易搞混,分段分析
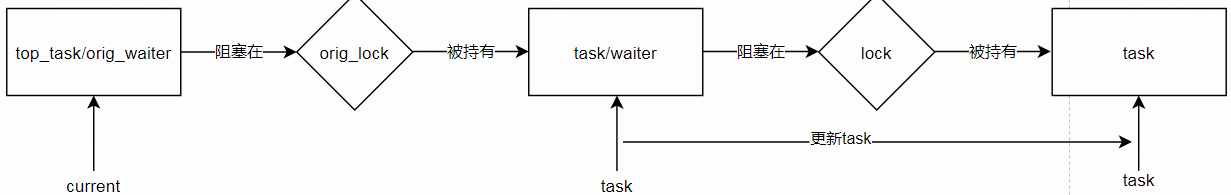
top_task/orig_waiter -----> [orig_lock] -----> task -----> [next_lock]
入参说明: task 拿着orig_lock,并且阻塞在next_lock; top_task/orig_waiter阻塞在orig_lock上
top_task/orig_waiter是这次新加入进来的task/waiter
static int rt_mutex_adjust_prio_chain(struct task_struct *task,
enum rtmutex_chainwalk chwalk,
struct rt_mutex *orig_lock,
struct rt_mutex *next_lock,
struct rt_mutex_waiter *orig_waiter,
struct task_struct *top_task)
{
struct rt_mutex_waiter *waiter, *top_waiter = orig_waiter;
struct rt_mutex_waiter *prerequeue_top_waiter;
int ret = 0, depth = 0;
struct rt_mutex *lock;
bool requeue = true; 默认需要重新入队,针对的是入参task,即orig_lock锁的owner;
这里的queue指的是task所等待的lock的进程红黑树队列,以优先级排序(即task->pi_blocked_on->lock->waiters)
如果使能了CONFIG_DEBUG_RT_MUTEXES,在当前这个调用路径上 detect_deadlock为真;否则就不检测死锁
bool detect_deadlock;
bool requeue = true;
detect_deadlock = rt_mutex_cond_detect_deadlock(orig_waiter, chwalk);
限制最大 walk chain 循环次数1024
不需要重新入队(!requeue)的时候会goto again继续检查下去
/*
* The (de)boosting is a step by step approach with a lot of
* pitfalls. We want this to be preemptible and we want hold a
* maximum of two locks per step. So we have to check
* carefully whether things change under us.
*/
again: // 不需要重新入队(!requeue)的时候会goto again继续检查下去
/*
* We limit the lock chain length for each invocation.
*/
if (++depth > max_lock_depth) {
static int prev_max;
/*
* Print this only once. If the admin changes the limit,
* print a new message when reaching the limit again.
*/
if (prev_max != max_lock_depth) {
prev_max = max_lock_depth;
printk(KERN_WARNING "Maximum lock depth %d reached "
"task: %s (%d)\n", max_lock_depth,
top_task->comm, task_pid_nr(top_task));
}
put_task_struct(task);
return -EDEADLK;
}
task->pi_lock 用来保护pi_waiters tree;
因为中断上下文也会获取该锁,所以其它上下文获取pi_lock时,需要禁中断
接着获取task对应的waiter;如果waiter为NULL,要么已经walk到链的尾部,要么有进程释放锁,链表状态有变
从这里开始,task 和对应的 waiter ,next_lock等变量,在后续循环检测中会沿着链表更新
/*
* We are fully preemptible here and only hold the refcount on
* @task. So everything can have changed under us since the
* caller or our own code below (goto retry/again) dropped all
* locks.
*/
retry:
/*
* [1] Task cannot go away as we did a get_task() before !
*/
raw_spin_lock_irq(&task->pi_lock);
/*
* [2] Get the waiter on which @task is blocked on.
*/
waiter = task->pi_blocked_on;
/*
* [3] check_exit_conditions_1() protected by task->pi_lock.
*/
/*
* Check whether the end of the boosting chain has been
* reached or the state of the chain has changed while we
* dropped the locks.
*/
if (!rt_mutex_real_waiter(waiter))
goto out_unlock_pi;
沿着链walk时检测各种变动
/*
* Check the orig_waiter state. After we dropped the locks,
* the previous owner of the lock might have released the lock.
*/
if (orig_waiter && !rt_mutex_owner(orig_lock)) // 如果 orig_lock的owner释放了orig_lock,则跳转
goto out_unlock_pi;
/*
* We dropped all locks after taking a refcount on @task, so
* the task might have moved on in the lock chain or even left
* the chain completely and blocks now on an unrelated lock or
* on @orig_lock.
*
* We stored the lock on which @task was blocked in @next_lock,
* so we can detect the chain change.
*/
if (next_lock != waiter->lock) // task之前还阻塞在next_lock上,现在如果next_lock != waiter->lock了,说明task有变动
goto out_unlock_pi;
/*
* Drop out, when the task has no waiters. Note,
* top_waiter can be NULL, when we are in the deboosting
* mode!
*/
if (top_waiter) { // 当前关注的调用链,本函数调用者是task_blocks_on_rt_mutex
if (!task_has_pi_waiters(task)) // 如果task上没有pi_waiters就跳出去(即owner可能已经释放了orig_lock以及其它lock)
goto out_unlock_pi;
/*
* If deadlock detection is off, we stop here if we
* are not the top pi waiter of the task. If deadlock
* detection is enabled we continue, but stop the
* requeueing in the chain walk.
*/
if (top_waiter != task_top_pi_waiter(task)) { //如果入参 top_waiter和task的top pi_waiter不是同一个进程,即orig/top_waiter不是orig_lock上优先级最高的waiter
if (!detect_deadlock)
goto out_unlock_pi; // 无需检测死锁就跳出
else
requeue = false; // 检测死锁的话就不需要重新入队,而是沿着链chain往前检查是否发生死锁
} // 是同一个进程,即current/top_waiter是orig_lock上优先级最高的waiter,owner优先级可能有调整,需要重新入队
}
/*
* If the waiter priority is the same as the task priority
* then there is no further priority adjustment necessary. If
* deadlock detection is off, we stop the chain walk. If its
* enabled we continue, but stop the requeueing in the chain
* walk.
*/
if (rt_mutex_waiter_equal(waiter, task_to_waiter(task))) { // 如果task对应的waiter 和原始状态相比没有变化,即task->prio没有被调整过
if (!detect_deadlock)
goto out_unlock_pi; // 无需检测死锁就跳出
else
requeue = false; // 检测死锁的话就不需要重新入队,而是沿着chain往前检查是否发生死锁
}
/*
* [4] Get the next lock
*/
lock = waiter->lock; //获取task等待的lock
/*
* [5] We need to trylock here as we are holding task->pi_lock,
* which is the reverse lock order versus the other rtmutex
* operations.
*/
if (!raw_spin_trylock(&lock->wait_lock)) { //获取wait_lock(保护该lock内部结构体字段) 如果trylock成功(拿到返回1,失败返回0),则释放pi_lock然后cpu_relax
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&task->pi_lock);
cpu_relax();
goto retry;
}
检测是否发生死锁,根据条件如果有必要的话
/*
* [6] check_exit_conditions_2() protected by task->pi_lock and
* lock->wait_lock.
*
* Deadlock detection. If the lock is the same as the original
* lock which caused us to walk the lock chain or if the
* current lock is owned by the task which initiated the chain
* walk, we detected a deadlock.
*/
if (lock == orig_lock || rt_mutex_owner(lock) == top_task) { // lock和orig_lock是同一把锁,或者lock的owner是top_task 说明发生死锁
debug_rt_mutex_deadlock(chwalk, orig_waiter, lock);
raw_spin_unlock(&lock->wait_lock);
ret = -EDEADLK;
goto out_unlock_pi;
}
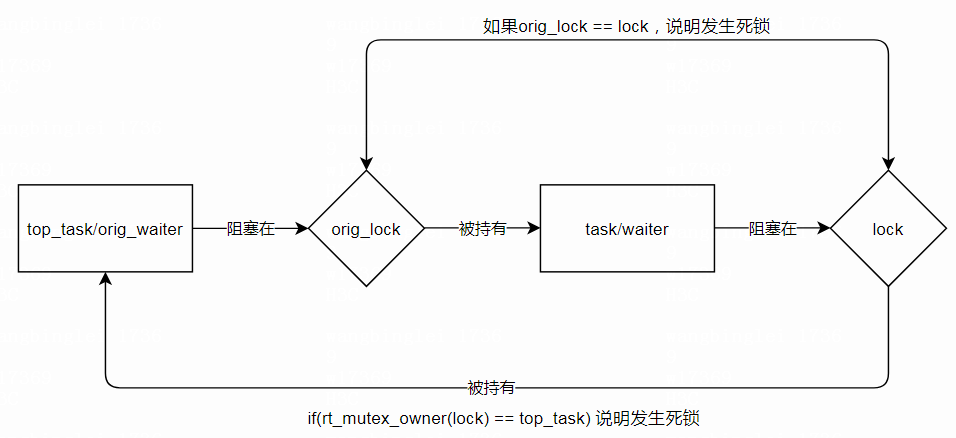
task不需要重新入队的话if(!requeue),就更新task和next_lock 继续沿着锁链往前检查goto again
/*
* If we just follow the lock chain for deadlock detection, no
* need to do all the requeue operations. To avoid a truckload
* of conditionals around the various places below, just do the
* minimum chain walk checks.
*/
if (!requeue) { //不需要重新入队,则继续沿着锁链往前检查
/*
* No requeue[7] here. Just release @task [8]
*/
raw_spin_unlock(&task->pi_lock);
put_task_struct(task);
/*
* [9] check_exit_conditions_3 protected by lock->wait_lock.
* If there is no owner of the lock, end of chain.
*/
if (!rt_mutex_owner(lock)) { //锁链到头了, lock没有owner就返回
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&lock->wait_lock);
return 0;
}
/* [10] Grab the next task, i.e. owner of @lock */
task = get_task_struct(rt_mutex_owner(lock)); // 继续沿着lock追踪下一个owner task
raw_spin_lock(&task->pi_lock);
/*
* No requeue [11] here. We just do deadlock detection.
*
* [12] Store whether owner is blocked
* itself. Decision is made after dropping the locks
*/
next_lock = task_blocked_on_lock(task); // 追踪下一个lock
/*
* Get the top waiter for the next iteration
*/
top_waiter = rt_mutex_top_waiter(lock); // lock上的top waiter
/* [13] Drop locks */
raw_spin_unlock(&task->pi_lock);
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&lock->wait_lock);
/* If owner is not blocked, end of chain. */
if (!next_lock) // next lock为NULL,即最新task没有阻塞在任何锁上,锁链到头了,直接跳出
goto out_put_task;
goto again; // 锁链还没到头,继续检查
}
task需要重新入队,根据task优先级,重新调整task->pi_blocked_on waiter在waiter->lock->waiters红黑树里的位置
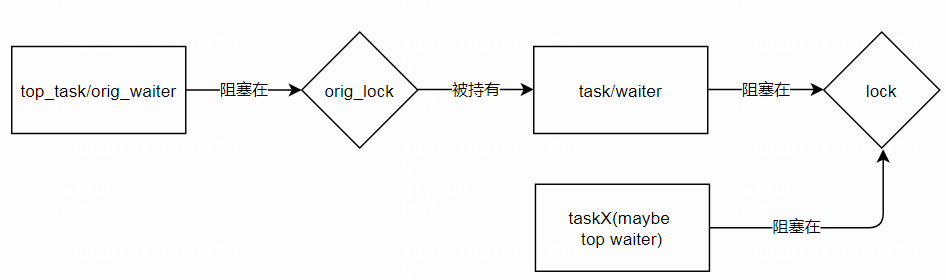
/*
* Store the current top waiter before doing the requeue
* operation on @lock. We need it for the boost/deboost
* decision below.
*/
prerequeue_top_waiter = rt_mutex_top_waiter(lock); // 暂存lock的的top waiter
/* [7] Requeue the waiter in the lock waiter tree. */ // task->pi_waiter_on指向的 waiter先退出lock->waiters红黑树队列
rt_mutex_dequeue(lock, waiter);
/*
* Update the waiter prio fields now that we're dequeued.
*
* These values can have changed through either:
*
* sys_sched_set_scheduler() / sys_sched_setattr()
*
* or
*
* DL CBS enforcement advancing the effective deadline.
*
* Even though pi_waiters also uses these fields, and that tree is only
* updated in [11], we can do this here, since we hold [L], which
* serializes all pi_waiters access and rb_erase() does not care about
* the values of the node being removed.
*/
waiter->prio = task->prio;
waiter->deadline = task->dl.deadline;
rt_mutex_enqueue(lock, waiter); // 再入队
/* [8] Release the task */
raw_spin_unlock(&task->pi_lock);
put_task_struct(task);
task->waiter->lock为NULL表明lock已经被释放或者没有竞争者
那么requeue之后lock的top waiter有变动的话,就唤醒这个最新的top waiter,函数返回.
/*
* [9] check_exit_conditions_3 protected by lock->wait_lock.
*
* We must abort the chain walk if there is no lock owner even
* in the dead lock detection case, as we have nothing to
* follow here. This is the end of the chain we are walking.
*/
if (!rt_mutex_owner(lock)) { // lock owner字段为NULL,walk不下去了
struct rt_mutex_waiter *lock_top_waiter;
/*
* If the requeue [7] above changed the top waiter,
* then we need to wake the new top waiter up to try
* to get the lock.
*/
lock_top_waiter = rt_mutex_top_waiter(lock);
if (prerequeue_top_waiter != lock_top_waiter) // requeue之后lock的top waiter更换了
rt_mutex_wake_waiter(lock_top_waiter); // 唤醒当前最新的那个top waiter
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&lock->wait_lock);
return 0;
}
更新task变量指向下一个task(taskA->lock->taskB,从指向taskA更新为指向taskB),增加task refcount引用计数
/* [10] Grab the next task, i.e. the owner of @lock */
task = get_task_struct(rt_mutex_owner(lock));
raw_spin_lock(&task->pi_lock);
如果task waiter是lock上优先级最高的waiter
那么把旧的top waiter从9步骤中更新后的task的pi_waiters红黑树上摘掉
把task waiter放进去,然后调整更新后的task的优先级
/* [11] requeue the pi waiters if necessary */
if (waiter == rt_mutex_top_waiter(lock)) { // task waiter 是lock waiters里进程优先级最高的那个
/*
* The waiter became the new top (highest priority)
* waiter on the lock. Replace the previous top waiter
* in the owner tasks pi waiters tree with this waiter
* and adjust the priority of the owner.
*/
rt_mutex_dequeue_pi(task, prerequeue_top_waiter); // 旧的top waiter从task的pi_waiters红黑树上摘掉
rt_mutex_enqueue_pi(task, waiter); // 新的top waiter放到task的pi_waiters红黑树上
rt_mutex_adjust_prio(task); // 调整task的优先级
如果task waiter是曾经是lock上优先级最高的waiter,但是现在已经不是了,
那么把旧的top waiter从9步骤中更新后的task的pi_waiters红黑树上摘掉,同时获取当前lock上的top waiter放进去
} else if (prerequeue_top_waiter == waiter) { // task waiter(task->pi_blocked_on)曾经是lock上的top waiter,但现在已经不是优先级最高的那个了
/*
* The waiter was the top waiter on the lock, but is
* no longer the top prority waiter. Replace waiter in
* the owner tasks pi waiters tree with the new top
* (highest priority) waiter and adjust the priority
* of the owner.
* The new top waiter is stored in @waiter so that
* @waiter == @top_waiter evaluates to true below and
* we continue to deboost the rest of the chain.
*/
rt_mutex_dequeue_pi(task, waiter); // 从task的pi_waiters红黑树上摘掉
waiter = rt_mutex_top_waiter(lock);
rt_mutex_enqueue_pi(task, waiter); // 把新的top waiter挂到 task的pi_waiters上
rt_mutex_adjust_prio(task); // 调整task的优先级
} else {
/*
* Nothing changed. No need to do any priority // 入参task waiter以前不是,现在也不是lock上优先级最高的那个,无需调整
* adjustment.
*/
}
更新next_lock,如果为空的话,跳出循环,函数返回
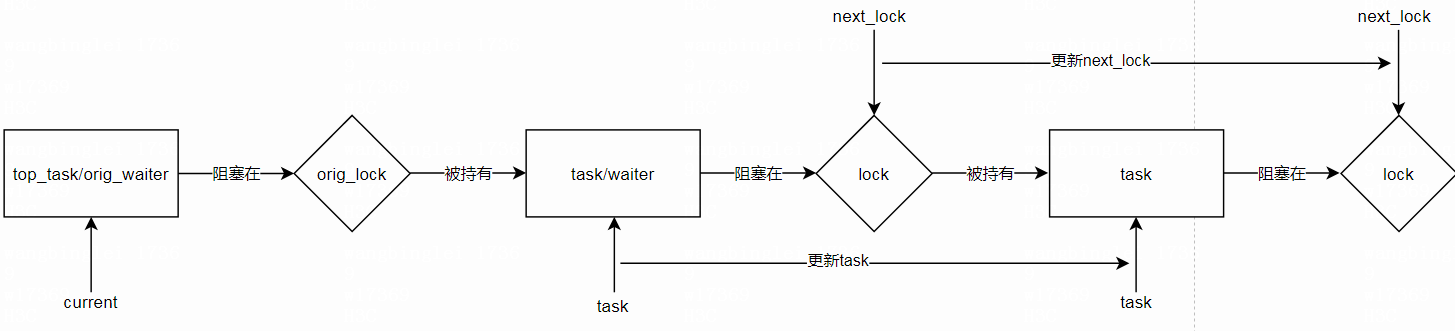
// 更新next_lock,
/*
* [12] check_exit_conditions_4() protected by task->pi_lock
* and lock->wait_lock. The actual decisions are made after we
* dropped the locks.
*
* Check whether the task which owns the current lock is pi
* blocked itself. If yes we store a pointer to the lock for
* the lock chain change detection above. After we dropped
* task->pi_lock next_lock cannot be dereferenced anymore.
*/
next_lock = task_blocked_on_lock(task);
/*
* Store the top waiter of @lock for the end of chain walk
* decision below.
*/
top_waiter = rt_mutex_top_waiter(lock);
/* [13] Drop the locks */
raw_spin_unlock(&task->pi_lock);
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&lock->wait_lock);
/*
* Make the actual exit decisions [12], based on the stored
* values.
*
* We reached the end of the lock chain. Stop right here. No
* point to go back just to figure that out.
*/
if (!next_lock) // 如果为空的话,跳出循环
goto out_put_task;
如果(!detect_deadlock && waiter != top_waiter) 跳出循环,函数返回
/*
* If the current waiter is not the top waiter on the lock,
* then we can stop the chain walk here if we are not in full
* deadlock detection mode.
*/
if (!detect_deadlock && waiter != top_waiter) // 不检测死循环,并且task的 waiter不是lock的top waiter,那么就跳出
goto out_put_task;
goto again; // 继续检查
out_unlock_pi:
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&task->pi_lock);
out_put_task:
put_task_struct(task);
return ret;
}
spin_unlock流程
释放锁的流程相对易读很多,看的是预编译后的代码
#define spin_unlock(lock) rt_spin_unlock(lock)
void __lockfunc rt_spin_unlock(spinlock_t *lock)
{
/* NOTE: we always pass in '1' for nested, for simplicity */
spin_release(&lock->dep_map, 1, _RET_IP_);
rt_spin_lock_fastunlock(&lock->lock, rt_spin_lock_slowunlock);
migrate_enable();
rcu_read_unlock();
sleeping_lock_dec();
}
rt_spin_lock_fastunlock
static inline __attribute__((__gnu_inline__)) __attribute__((__unused__)) __attribute__((__no_instrument_function__))
void rt_spin_lock_fastunlock(struct rt_mutex *lock, void (*slowfn)(struct rt_mutex *lock))
{
if (__builtin_expect(!!((({ typeof(&lock->owner) __ai_ptr = (&lock->owner); // lock->owner是个struct task_struct *类型,再取一次地址,所以__ai_ptr是个二级指针
kasan_check_write(__ai_ptr, sizeof(*__ai_ptr));
({ __typeof__(*(__ai_ptr)) __ret;
__ret = (__typeof__(*(__ai_ptr))) __cmpxchg_rel((__ai_ptr), (unsigned long)(get_current()), (unsigned long)(((void *)0)), sizeof(*(__ai_ptr))); //
__ret; }); }) // __ret 是lock->owner字段的值,
== get_current())), 1)) // 期望owner是当前进程,如果lock->owner == current,说明当前task自己就是owner,即没有任何waiters
return;
else
slowfn(lock); // 如果owner不是 current 说明lock被高优先级的task偷走了steal,即有高优先级的task在等锁,而自己的优先级已经被boosted了,所以在自己释放lock之前还要走慢速流程deboost自己的优先级
}
rt_mutex_postunlock
void rt_mutex_postunlock(struct wake_q_head *wake_q,
struct wake_q_head *wake_sleeper_q)
{
// 先唤醒
wake_up_q(wake_q);
wake_up_q_sleeper(wake_sleeper_q);
// 再开抢占
do { __asm__ __volatile__("": : :"memory"); if (__builtin_expect(!!(({ preempt_count_sub(1); should_resched(0); })), 0)) preempt_schedule(); } while (0);
}
rt_spin_lock_slowunlock
void __attribute__((__section__(".sched.text"))) rt_spin_lock_slowunlock(struct rt_mutex *lock)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct wake_q_head wake_q = { ((struct wake_q_node *) 0x01), &wake_q.first };
struct wake_q_head wake_sleeper_q = { ((struct wake_q_node *) 0x01), &wake_sleeper_q.first };
bool postunlock;
do { ({ unsigned long __dummy; typeof(flags) __dummy2; (void)(&__dummy == &__dummy2); 1; }); flags = _raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&lock->wait_lock); } while (0);
postunlock = __rt_mutex_unlock_common(lock, &wake_q, &wake_sleeper_q);
do { ({ unsigned long __dummy; typeof(flags) __dummy2; (void)(&__dummy == &__dummy2); 1; }); _raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&lock->wait_lock, flags); } while (0);
if (postunlock)
rt_mutex_postunlock(&wake_q, &wake_sleeper_q);
}
__rt_mutex_unlock_common
static bool __attribute__((__section__(".sched.text"))) __rt_mutex_unlock_common(struct rt_mutex *lock,
struct wake_q_head *wake_q,
struct wake_q_head *wq_sleeper)
{
do { (void)(&lock->wait_lock); } while (0);
do { } while (0);
if (!rt_mutex_has_waiters(lock)) { // 没有waiter了
lock->owner = ((void *)0);
return false;
}
mark_wakeup_next_waiter(wake_q, wq_sleeper, lock); // 存在waiters,那么需要唤醒一个进程
return true;
}
mark_wakeup_next_waiter
// 标记需要接下来唤醒的waiter,放到唤醒队列中;同时更新current优先级
static void mark_wakeup_next_waiter(struct wake_q_head *wake_q,
struct wake_q_head *wake_sleeper_q,
struct rt_mutex *lock)
{
struct rt_mutex_waiter *waiter;
_raw_spin_lock(&get_current()->pi_lock);
waiter = rt_mutex_top_waiter(lock);
rt_mutex_dequeue_pi(get_current(), waiter); // top waiter从cureent->pi_waiters出队列
rt_mutex_adjust_prio(get_current()); // 调整current的优先级, 更新current->pi_top_task
lock->owner = (void *) RT_MUTEX_HAS_WAITERS; // 为了防止低优先级的进程偷走锁,这里需要设置标记 RT_MUTEX_HAS_WAITERS
do { preempt_count_add(1); __asm__ __volatile__("": : :"memory"); } while (0); // 避免出现优先级反转,即避免top waiter被抢占,所以这里先关抢占
// 加到唤醒队列,稍后rt_mutex_postunlock 会唤醒该waiter
if (waiter->savestate)
wake_q_add_sleeper(wake_sleeper_q, waiter->task);
else
wake_q_add(wake_q, waiter->task);
__raw_spin_unlock(&get_current()->pi_lock);
}
rt_mutex_wake_waiter
static void rt_mutex_wake_waiter(struct rt_mutex_waiter *waiter)
{
if (waiter->savestate)
wake_up_lock_sleeper(waiter->task);
else
wake_up_process(waiter->task);
}
参考索引
Internals of the RT Patch
rt-mutex-design
linux-5.4.74